Global Infrastructure
Reference URL : https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/global-infrastructure/
Hierarchy
- Geography
- Regions
- Availability Zones
- Data Centers
- Availability Sets
- Virtual Machines
- Availability Sets
- Data Centers
- Availability Zones
- Regions

Quick Questions
How many Regions can be in a geography?
A geography contains at least one Azure region.
India is Geography and it has 3 regions
- Central India (Pune)
- South India (Chennai)
- West India (Mumbai)
How many Availability Zones ins a region?
A region may contain more than one availability zones. In general a Region contains 3 availability Zone. E.g. Central India Region has 3 Availability Zones.










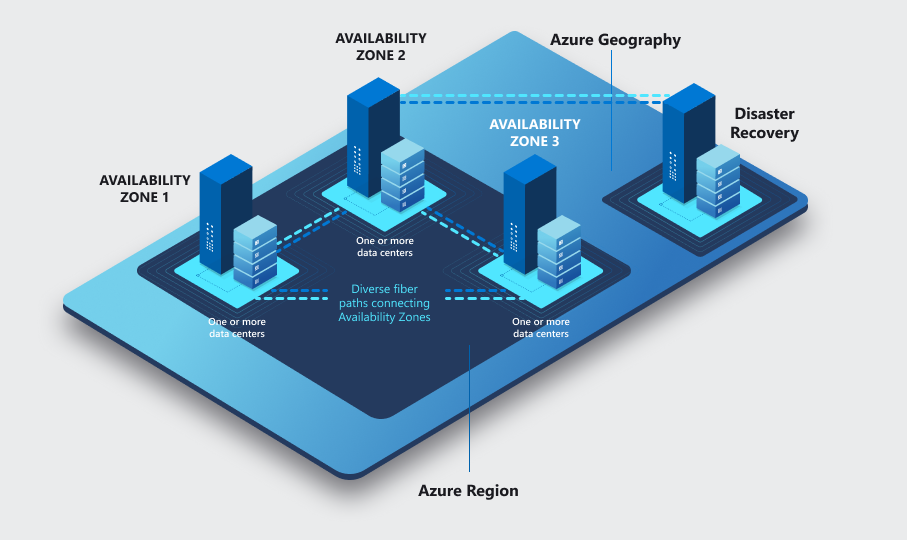
Geography
Containing at least one or more regions
An Azure geography is a discrete (पृथक) market, typically containing at least one or more regions, that preserves data residency and compliance boundaries.
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/global-infrastructure/geographies/#geographies
An area of the world that contains at least one Azure region . Geographies define a discrete market that preserves data-residency and compliance boundaries. Geographies allow customers with specific data-residency and compliance needs to keep their data and applications close. Geographies are fault tolerant to withstand complete region failure through their connection to our dedicated high-capacity networking infrastructure.
Azure Geography some Example :
- Asia-Pacific
- Australia
- Brazil
- Canada
- China
- Europe
- France
- Germany
- India
- Japan
- Korea
- North America
- Norway
- South Africa
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- UK
- United Arab Emirates
- US Department of Defense
- US Government
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-in/azure/availability-zones/cross-region-replication-azure
Region
Group of multiple data centers
A region may contain more than one availability zones. In general a Region contains 3 availability Zone. E.g. Central India Region has 3 Availability Zones.
A set of datacenters deployed within a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network.
Recommended Region
A region that provides the broadest range of service capabilities and is designed to support availability zones now, or in the future. These regions are designated in the Azure portal as Recommended.
Alternate (other) Region
A region that extends Azure’s footprint within a data-residency boundary where a recommended region also exists. Alternate regions help to optimize latency and provide a second region for disaster recovery needs. They aren’t designed to support availability zones, although Azure conducts regular assessment of these regions to determine if they should become recommended regions. These regions are designated in the Azure portal as Other.
Special Azure Regions
Azure has some special regions that you may wish to use when building out your applications for compliance or legal purposes . These special regions include:
US Gov Virginia and US Gov Iowa A physical and logical network-isolated instance of Azure for US government agencies and partners, operated by screened US persons. Includes additional compliance certifications such as FedRAMP and DISA. Read more about Azure Government.
China East and China North These regions are available through a unique partnership between Microsoft and 21Vianet, whereby Microsoft does not directly maintain the datacenters. See more about Azure China 21Vianet.
Germany Central and Germany Northeast These regions are available via a data trustee model whereby customer data remains in Germany under control of T-Systems, a Deutsche Telekom company, acting as the German data trustee.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/regions#special-azure-regions
cross-region replication (formerly paired region)
A reliability strategy and implementation that combines high availability of availability zones with protection from region-wide incidents to meet both disaster recovery and business continuity needs.

Availability Zone
Each zone is composed of one or more datacenters
Azure Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region and offer high availability to protect your applications and data from datacentre failures.
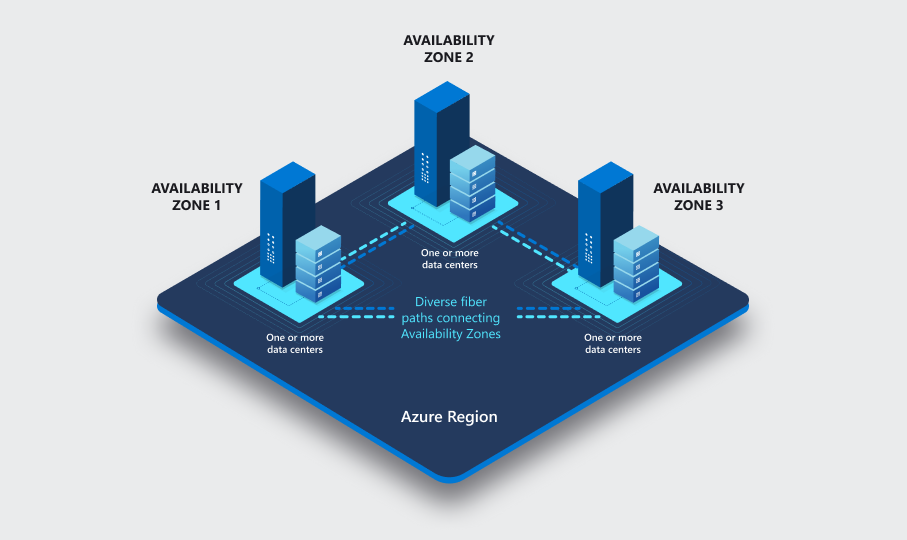
Each zone is composed of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure.
Each zone is composed of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. Availability zones are designed so that if one zone is affected, regional services, capacity, and high availability are supported by the remaining two zones.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
Data Center
An Azure data center is a unique physical building that contains thousands of physical servers with it’s own power, cooling and networking infrastructure. These data ceneters are located all over the globe
Data Center Physical Isolation
Azure strives to ensure a minimum distance of 300 miles (483 kilometers) between datacenters in enabled regions, although it isn’t possible across all geographies . Datacenter separation reduces the likelihood that natural disaster, civil unrest, power outages, or physical network outages can affect multiple regions. Isolation is subject to the constraints within a geography, such as geography size, power or network infrastructure availability, and regulations.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/cross-region-replication-azure
Availability Sets
Availability Sets takes the virtual machine and configures multiple copies of it. Each copy is isolated within a separate physical server, compute rack, storage units and network switches within a single datacentre within an Azure Region.
How do availability sets work?
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/availability-set-overview
How do availability sets work?
Each virtual machine in your availability set is assigned an update domain and a fault domain by the underlying Azure platform. Each availability set can be configured with up to three fault domains and twenty update domains . Update domains indicate groups of virtual machines and underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time. When more than five virtual machines are configured within a single availability set with five update domains, the sixth virtual machine is placed into the same update domain as the first virtual machine, the seventh in the same update domain as the second virtual machine, and so on. The order of update domains being rebooted may not proceed sequentially during planned maintenance, but only one update domain is rebooted at a time. A rebooted update domain is given 30 minutes to recover before maintenance is initiated on a different update domain.
Fault domains define the group of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch. By default, the virtual machines configured within your availability set are separated across up to three fault domains. While placing your virtual machines into an availability set does not protect your application from operating system or application-specific failures, it does limit the impact of potential physical hardware failures, network outages, or power interruptions.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/availability-set-overview
Fault Domain
Each availability set can be configured with up to three fault domains.

Update Domain
Each availability set can be configured with up to twenty update domains.
The Spectrum of Azure High Availability Options
Single VM => Availability Sets => Availability Zones => Region Pairs
Single VM—running a Virtual Machine (VM) on Azure with no replication.
Availability Sets—running a VM with one or more replicated copies on separate hardware within the same Availability Zone, providing resiliency against machine failure.

foundational service
A core Azure service that’s available in all regions when the region is generally available.